Rabbit Care & Husbandry
Rabbits are fluffy, inquisitive and adorable companions! Before introducing these wonderful creatures into your home, it is important to know that rabbits have very specific husbandry and dietary requirements that greatly impact their overall health and wellbeing. Most diseases and health problems can be avoided with the right care and set up at home.
We provide several veterinary services to keep your bunnies healthy, happy and hopping!
The following veterinary services are available at Berwick Clyde Vet:
- General health checks
- Basic emergency, medical and surgical treatments
- Hospitalisation
- Vaccination services (annual Filavac vaccine)
- Desexing
- Nutritional and husbandry advice
- Nail trims
- Parasite prevention
- Referral to exotic pet specialist
We work in association with several exotic pet clinics to provide the best care and advice for your rabbit. For cases that are not able to be managed in clinic, referral to an exotic pet specialist can be organised on your behalf.

Vaccination
Just like cats and dogs, rabbits need annual vaccinations. At Berwick Clyde Vet, we vaccinate pet rabbits against both type 1 and 2 Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus (RHDV), a deadly disease.
RHDV can spread through contact with infected rabbits’ urine, faeces (including from contact with the bottom of your shoes!), saliva, or mosquitos.
The Filavac® vaccination provides maximum protection, starting at 10 weeks of age. With Filavac®, your rabbit gains immunity in just 7 days after injection, lasting for 12 months with an annual booster.
Ensure your bunny’s well-being, schedule their Filavac vaccination today!

Desexing
Berwick Clyde Vet provides routine desexing for both male and female rabbits.
Desexing your pet rabbit is beneficial for reducing risks of ovarian and uterine cancer, inter-rabbit aggression, sexually driven behaviours and unwanted pregnancy.
Rabbits reach sexual maturity when they reach approximately 75% of their adult body weight, which means small breeds will become fertile earlier. Small breed rabbits can reach sexual maturity at approximately 4 – 5 months of age and larger breeds 5 – 8 months.
We recommend desexing female rabbits 6 months of age and male rabbits 4 months. In some circumstances smaller breeds such Netherland Dwarfs should wait until they are 12-24 months before desexing or at least 1kg in weight.
Our desexing package for rabbits are inclusive of:
- Physical exam with the veterinarian to assess your pet’s suitability to undergo an anaesthetic.
- IV Fluid Therapy to maintain your rabbit’s blood pressure and hydration whilst under the anaesthetic. This also aids in a smoother recovery and allows easy vein access.
- Anaesthesia which has a sedative and a pain relief component to help keep your pet calm and comfortable before, during and after their surgery.
- Surgery to desex your pet inclusive of dissolvable sutures.
- Incubator equipped with temperature control and piped oxygen.
- Nursing Care post op until your rabbit is up and eating on their own.
- Pain relief injection and take-home medication to ensure that your pet is free of pain straight after the surgery and for the next seven days until the wound has healed.
- Critical Care which is a specially formulated food for rabbits and guinea pigs given to help gut movement which is critical in these guys. It is administered by your pet’s nurse when they have woken from surgery and continues until they are eating on their own and ready to go home.
- A free revisit in 7-10 days’ time to check the wound and make sure it has healed well. If you have any concerns before this time, we are more than happy to offer a recheck sooner as well as ongoing phone support should we need to chat.
Our de-sexing surgeries are performed on weekdays with an admission time between 8am and 9am and discharge time generally from 5pm onwards to allow them time to recover (or sooner if they’re up and eating well).

Husbandry
Rabbits should always have plenty of space with a minimum floor space of 1.5m x 1.5m per rabbit. The minimum recommended enclosure size for a pair of average size rabbits is 3m x 2m x 1m according to the Rabbit Welfare Association and Fund.
Outdoors
Ideally rabbits should be housed inside but we understand this may not always be feasible for every family.
Outdoor rabbits should be housed in a hutch or playpen, ideally in a sheltered garden area protecting them from the elements. As rabbits are sensitive to extreme temperatures, especially heat, ensure temperatures don’t exceed 28 degrees Celsius to avoid heat exhaustion. Provide ample water and shade on hot days, and consider placing frozen water bottles in the pen for cooling. To prevent mosquito-transmitted diseases like calicivirus and myxomatosis, insect-proof the enclosures with flyscreen or netting. Regularly clean and dry the enclosure, changing newspaper flooring or hay bedding weekly to prevent toxic waste buildup.
Indoors
Rabbits are wonderful indoor pets for various reasons. They enjoy socializing with humans, making them great companions. Indoor living protects them from harsh weather and predators, resulting in a longer lifespan. Litter-training is manageable, and indoor settings offer more opportunities for play, bonding, and enrichment with their owners.
Indoor rabbits can either have a designated room or access to the entire house. Before giving them freedom, rabbit-proof your home! Cover or hide electrical wires, avoid toxic plants, supervise interactions with other pets, and block escape routes.
Initially, confine your rabbit to a small area for security and toilet training. Use large, hay-lined litter trays, providing one per rabbit plus an extra to prevent aggression. Once they feel comfortable, gradually introduce them to other areas. Choose easily cleanable flooring to avoid slipperiness and pressure sores. Enrich their environment with cardboard boxes, soft tunnels, and ramps for play and hiding.

Nutrition
Nutrition is imperative to your rabbit’s gastrointestinal and dental health. Most health problems commonly seen in rabbits are caused by feeding an inappropriate or poor-quality diet.
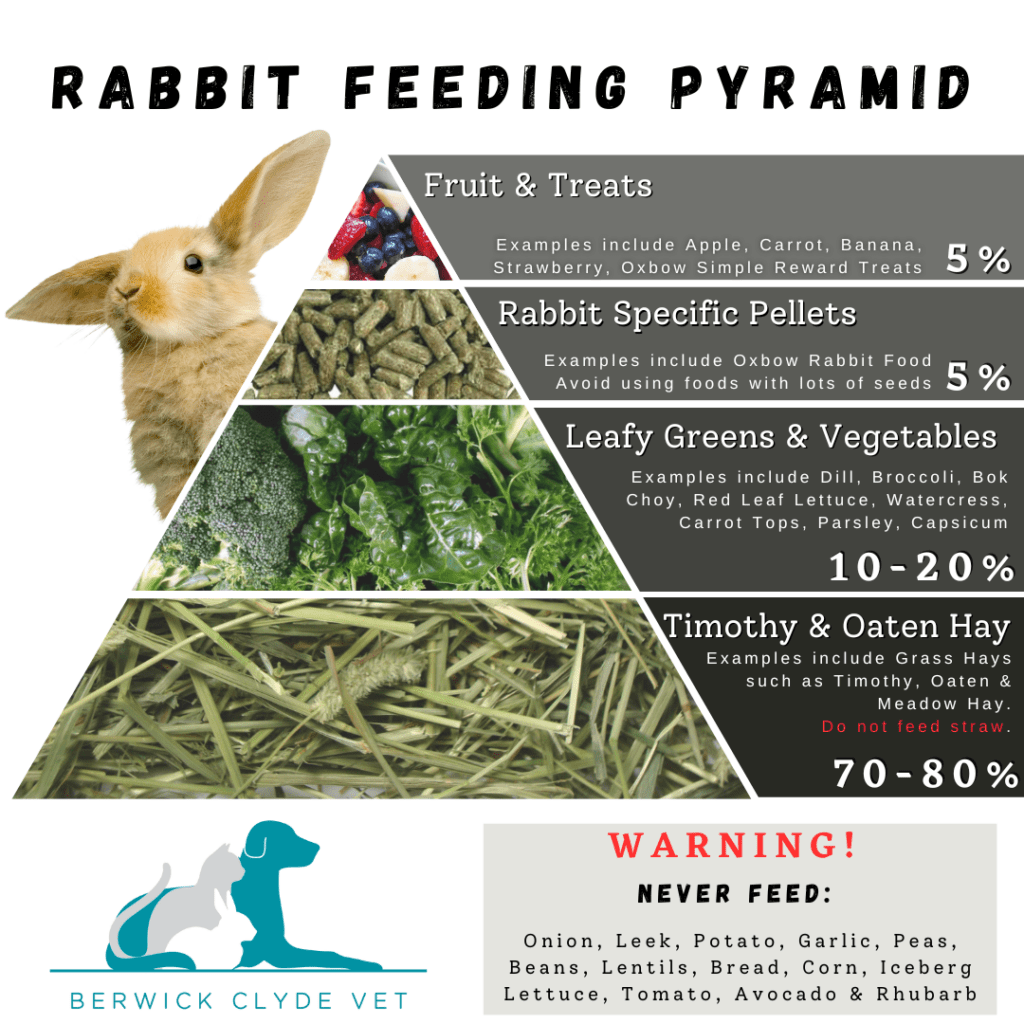
Recommended Diet for Rabbits
- Hay: Provide unlimited access to good quality hay or grass hay (such as Timothy, Oaten, or Teff hay). A 2kg rabbit should eat a cat litter tray’s worth of hay daily. Hay should make up 70-80% of their total diet.
- Fresh Vegetables and Herbs: Offer a variety of fresh vegetables and herbs, such as Asian greens, cabbage, broccoli, coriander, carrot tops, celery leaves, silver beet, parsley, mint, basil, watercress, milk thistle, cucumber, and cauliflower. These should make up 10-20% of their diet.
- High Fiber Pellets: Include a small amount of good high-fiber pellets in their diet, about a tablespoon per rabbit per day, accounting for 5% of their total food intake.
- Treats: Offer treats in moderation, such as fruits like banana, apple, pear, strawberries, watermelon, grapes, and capsicum. Also, you can provide a handful of carrots, almonds (1-2), sultanas (up to 5), cranberries (up to 5), and fresh or dried rose petals. Treats should make up 5% of their diet.
Remember to maintain a balanced diet and avoid overfeeding treats to keep your rabbits healthy and happy!
Rabbits should have access to daily fresh water. Water can be dispensed in either a dripper bottle or via a water bowl, you can even do both! Make sure the water bowl is heavy so that it cannot be easily knocked over!
